This section of the Handbook on Notification Requirements covers the notification obligations under the AGREEMENT ON TECHNICAL BARRIERS TO TRADE. It consists of the following five parts:
For Members which acceded pursuant to Article XII of the Marrakesh Agreement, their respective Protocols of Accession may contain notification obligations in addition to those set out in the WTO Agreements, and may govern the deadlines for the submission of their initial notifications.
The WTO Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade seeks to ensure that technical regulations, standards and conformity assessment procedures do not create unnecessary obstacles to trade. Transparency through specific notifications obligations is one of the principles under the Agreement to minimize trade barriers. WTO Members are subject to different kinds of notifications requirements:
Technical Regulations (Article 2.9.2) and Urgent Technical Regulations (Article 2.10.1); Conformity Assessment Procedures (Article 5.6.2) and Urgent Conformity Assessment Procedures (Article 5.7.1)
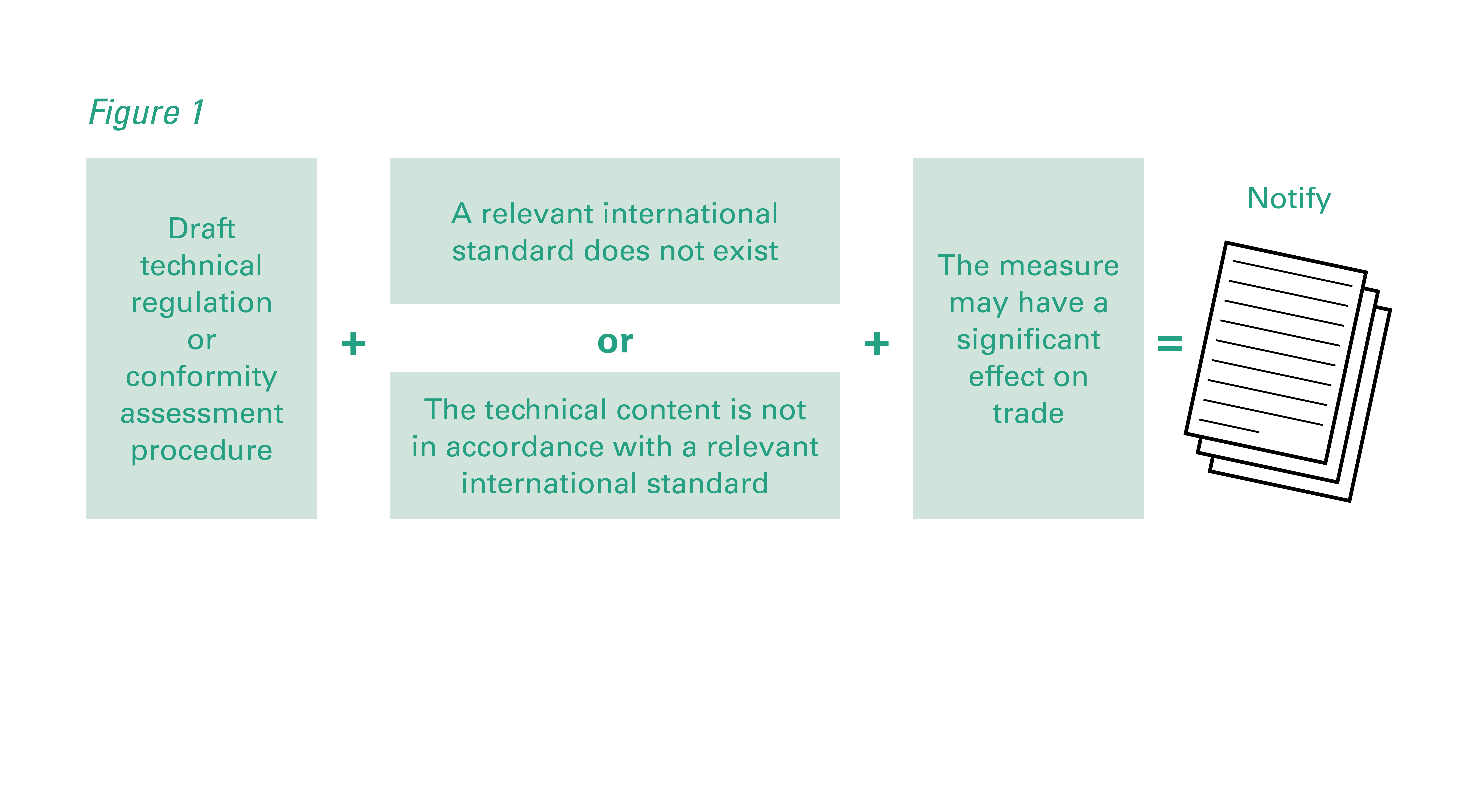
The notification process ordinarily begins by identifying those measures that should be notified to the WTO. Figure 1 illustrates whether to notify technical regulations and conformity assessment procedures in line with Articles 2.9 and 5.6 of the TBT Agreement.

The notification should include information on products to be covered as well as on objective and rationale of the measure. In addition, it should provide a comment period (normally 60 days), except in urgent circumstances (Articles 2.10.1 and 5.7.1).
Over the years, the TBT Committee has adopted a series of recommendations related to the implementation of notification obligations contained in the TBT Agreement. These can be found under the transparency chapter of G/TBT/1 (see latest Revision) and are also explained in the TBT Enquiry Point Guide.
Statement of Implementation
Article 15.2 of the TBT Agreement commits Members to submit a Statement of Implementation on the measures in existence or taken to ensure the implementation and administration of the Agreement, including the provisions on transparency. This one- time notification requirement should include information covering legislative, regulatory and administrative action taken so as to ensure that the provisions of the Agreement are applied. If the Agreement itself has been incorporated into domestic law, the statement should indicate how this has been done. The statement should also indicate the entities designated as the Enquiry Point(s) (Article 10.1-3) and the Notification Authority (Article 10.10) for that Member.
Agreements with other Members
Article 10.7 Members may reach agreement with other countries on issues related to technical regulations, standards or conformity assessment procedures. These can include mutual recognition agreements, equivalence agreements and other types of regulatory co-operation mechanisms. These agreements, if they may have a significant effect on trade, should be notified, through the Secretariat, by one of the Members party to the agreement, indicating the products to be covered and a brief description of the agreement.
Notifications under Paragraph C and Paragraph J of the Code of Good Practice on the Preparation, Adoption and Application of Standards (Annex 3 to the Agreement)
The TBT Agreement's "Code", provides, among others (and through Article 4 of the Agreement), that Members shall ensure that their central government standardizing bodies accept and comply with the Code. Also, Members need to take such reasonable measures as may be available to them to ensure that local government and non-governmental standardizing bodies within their territories, as well as regional standardizing bodies, of which they or one or more bodies within their territories are Members, accept and comply with the Code.
Standardizing bodies that have accepted or withdrawn from the Code (Annex 3) must notify this fact to the ISO via email tbtcode@iso.org. Those bodies that have accepted the Code are required to publish a work programme every six months, and its existence must also be notified through the same email address.
All WTO Members.
Technical Regulations and Conformity Assessment Procedures
At an early appropriate stage when amendments can still be introduced, and comments taken into account. Figure 2 below indicates the lifecycle of a measure.
Figure 2: The lifecycle of a measure

Statement of Implementation
Article 15.2 Upon accession to the WTO. Revisions submitted as necessary when there are relevant changes in the regulatory process.
Agreements with other Members
Article 10.7 When a Member has reached agreement with another Member on issues related to technical regulations, standards or conformity assessment procedures.
Acceptance of the Code of Good Practice
Notification of work programmes
Every six months. Alternatively, the website address where work programmes are regularly made available should be provided.
The ePing SPS&TBT Platform helps manage and track technical barriers to trade (TBT) and sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) measures. ePing allows for better national coordination with regulatory agencies, helps keep track of all notifications submitted and gives access to comprehensive TBT and SPS transparency related information across the Membership on one website. To access the notification submission services, government officials responsible for the preparation and submission of notifications should register on the ePing platform and send a message to ePing@wto.org requesting notification admin rights. A notification admin can, in addition to submitting notifications, also grant notification drafting rights and/or submission rights to other domestic users and update Enquiry Point contact details. Users with a WTO account can use these credentials to register on the site and benefit from the single sign-on across WTO websites. While Members can submit notifications by email to the Central Registry of Notifications (CRN) (crn@wto.org), there is a significantly longer circulation delay as these have to be processed manually by the WTO Secretariat. Notification templates can be downloaded from the TBT Transparency toolkit. Questions and queries on the ePing SPS&TBT Platform can be sent to the WTO Secretariat (ePing@wto.org).
Notifications under Paragraph C and Paragraph J of the Code of Good Practice on the Preparation, Adoption and Application of Standards (Annex 3 to the Agreement)
Standards-related notifications need to be submitted to the ISO via email tbtcode@iso.org. The WTO ISO Standards Information Gateway contains the full list of standardizing bodies that have accepted the Code as well as information on their work programmes. The notification formats for acceptance (Form A), withdrawal (Form B) and work programmes (Form C) can also be downloaded through the Gateway. Acceptance and withdrawal notifications are subsequently circulated by the WTO Secretariat. These notifications can be consulted in the Facts & figures tab on ePing in each Members' profile page.
| WHAT MUST BE NOTIFIED? | WHICH MEMBERS MUST NOTIFY? | WHEN TO NOTIFY? | HOW TO NOTIFY? | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Notification requirements | Type of measure | Members notifying | Periodicity | Comments on Periodicity | Format | To whom 3 | Notification Symbol | |
| 1. | Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade, Article 2.9. | Technical regulations. | All WTO Members | Ad hoc | Yes (Submissions of notifications) | WTO Secretariat | G/TBT/N/* | |
| 2. | Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade, Article 2.10. | Technical regulations (urgent). | All WTO Members | Ad hoc | Yes (Submissions of notifications) | WTO Secretariat | G/TBT/N/* | |
| 3. | Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade, Article 3.2. | Technical regulations - local government (urgent or non- urgent). | All WTO Members | Ad hoc | Yes (Submissions of notifications) | WTO Secretariat | G/TBT/N/* | |
| 4. | Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade, Article 5.6. | Conformity assessment procedures. | All WTO Members | Ad hoc | Yes (Submissions of notifications) | WTO Secretariat | G/TBT/N/* | |
| 5. | Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade, Article 5.7. | Conformity assessment procedures (urgent). | All WTO Members | Ad hoc | Yes (Submissions of notifications) | WTO Secretariat | G/TBT/N/* | |
| 6. | Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade, Article 7.2. | Conformity assessment Procedures-local Government (urgent or non-urgent). | All WTO Members | Ad hoc | Yes (Submissions of notifications) | WTO Secretariat | G/TBT/N/* | |
| 7. | Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade, Article 10.7. | Bilateral agreements; technical regulations; conformity assessment procedures; standards. | All WTO Members | Ad hoc | Yes (Submissions of notifications) | WTO Secretariat | G/TBT/10.7/N/* | |
| 8. | Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade, Article 15.2. | Administrative arrangements; laws/regulations measure in existence or taken to ensure the implementation and administration of the TBT Agreement. | All WTO Members | One time | Upon entry into force of the WTO Agreement. Subsequent revisions as necessary. | No (There is no specific format. Examples are available on TBT IMS) | Committee on Technical Barriers to Trade | G/TBT/2/* |
| 9. | Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade, Annex 3 paragraph C. | Acceptance of/ withdrawal from a code (Code of Good Practice for the Preparation, Adoption and Application of Standards). | Standardizing Bodies accepting the Code/ withdrawing from the code. | One time | Yes (Acceptance (Form A) Withdrawal (Form B)) | WTO ISO Standards Information Gateway | G/TBT/CS/N/* | |
| 10. | Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade, Annex 3 paragraph J. | Work programmes on standardization activities. | Standardizing Bodies accepting the Code. | Regular – Semi-annual | Every 6 months. Alternatively, a direct link to a website address where work programmes are published regularly can be provided. | Yes (Form C WTO ISO Standards Information Gateway) | WTO ISO Standards Information Gateway | G/TBT/CS/N/* |
Recommendation of the TBT Committee on Coherent Use of Notification Formats G/TBT/35/Rev.1.
Decisions and recommendations adopted by the Committee since 1 January 1995 G/TBT/1/Rev.14 (or latest Revision), Chapter 5.3.
WTO TBT Enquiry Point Guide- Making transparency work: Guide designed for training and capacity-building purposes and developed in response to a request by the Committee on Technical Barriers to Trade (the "TBT Committee"), at the end of 2015, that the WTO Secretariat prepare a guide on best practices for enquiry points.
WTO Members' transparency toolkit: The TBT webpage containing information on notification obligations, formats to be used, decisions and recommendations adopted by the TBT Committee since 1 January 1995, handbooks, step-by-step manuals, links to Members' TBT Enquiry Points websites, and other aids for Members' transparency work in TBT.
WTO TBT Booklet: The TBT booklet includes an overview of the TBT Agreement, work of the TBT Committee, disputes invoking provisions of the Agreement, frequently asked questions, the full legal text of the Agreement, as well as the decisions and recommendations adopted by the TBT Committee since 1 January 1995.
TBT Information Management System: The database containing all TBT notifications from Members, standards-related information, all specific trade concerns raised in the TBT Committee, contact details of Members Enquiry Points, and otherTBT related documents.
TBT Notification Submission System: The TBT NSS is a password-protected on-line notification system allowing Members to complete and submit notifications using a simple to use platform. For further details and to request access send an email to tbt@wto.org.
ISO WTO Standards Information Gateway: The WTO-ISO Standards Information Gateway contains the full list of standardizing bodies that have accepted the Code as well as information on their work programmes.
ePing: The SPS/TBT export alert system allows stakeholders to keep track of product requirements in foreign markets. This includes a specific feature which enables enquiry points to manage national subscribers, send emails and activate a discussion forum on notifications within their country.
To find a list of notifications on TBT go to the TBT IMS. This is a comprehensive database allowing users to search all TBT notifications and Specific Trade Concerns raised in the TBT Committee (STCs). Users can also browse information on TBT Enquiry Points, Statements on Implementation, Agreements between Members and other TBT-related documents.
Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade LT/UR/A-1A/10.
1 The WTO TBT Enquiry Point Guide provides a consolidated and comprehensive list of transparency obligations and recommendations related to the implementation of the TBT Agreement.
2 All notifications, regardless of their subject content or the requirement under which they are being submitted, must be directed to the administrator of the Central Registry of Notifications (CRN), as indicated in document WT/INF/25/Rev.2. TBT notifications may be submitted through online submission systems or as electronic attachments to emails. As it may be practice, a copy of the notification may be sent to the Secretariat unit substantially handling the notification.
3 All notifications, regardless of their subject content or the requirement under which they are being submitted, must be directed to the administrator of the Central Registry of Notifications (CRN), as indicated in document WT/INF/25/Rev.2. Notifications may be submitted through online submission systems, as electronic attachments to emails or on paper. As it may be practice, a copy of the notification may be sent to the Secretariat unit substantially handling the notification.
World Trade Organization
The texts and materials published on this website serve a purely informative purpose and have no official or legal status. The information published on this website does not constitute a legal interpretation of relevant notification provisions, and it is without prejudice to WTO Members' rights and obligations. In particular, it has no legal implications with regards to Members' compliance with relevant notification provisions or the WTO-conformity of any notified measures. Terminology used on this website, including terms reproduced in the notifications referenced therein, do not involve any judgment, official endorsement or acceptance by the WTO as to the legal status of any territory, and have no implications for the issue of sovereignty.